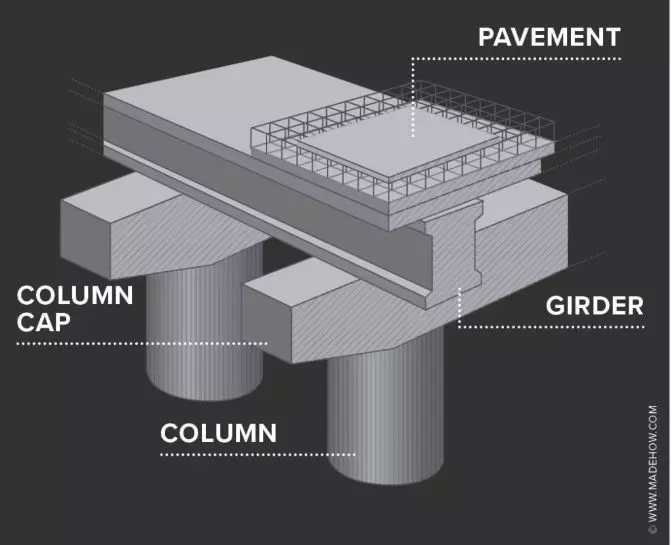
Bridge inspections are a critical process that helps engineers detect small defects and potential issues before they become major problems. These inspections ensure the safety of bridges, which are vital to our daily lives and transportation systems. If a problem in a bridge is not identified early, it could lead to serious consequences, including structural failure, collapse, and even loss of life. That’s why bridge inspections are required by law in many countries around the world. This guide will cover what bridge inspections involve, the different types and techniques used, the challenges inspectors face, regulatory requirements, and how modern technology like drones can make the process safer and more efficient. Whether you're an engineer, a student, or simply curious about infrastructure, this article provides a comprehensive overview of bridge inspections and their importance in maintaining public safety. While most people don’t think much about the bridges they drive over every day, millions of bridges across the globe are in constant use and require regular maintenance. In the U.S. alone, there are over 700,000 bridges, all of which must be inspected regularly to ensure they remain safe for public use. Although practices and regulations vary from country to country, most require bridges to be inspected at least once every two years. During these inspections, engineers look for any signs of wear, damage, or structural issues that might require attention. The traditional method involves using a snooper truck, also known as a bucket truck, which allows inspectors to access hard-to-reach areas under the bridge. These trucks can climb steep inclines and operate in deep water, making them essential tools for traditional inspections. These vehicles allow inspectors to lower a bucket down to get a close-up view of the bridge's underside, ensuring that no critical area is overlooked. However, such methods come with logistical and safety challenges that have led to the adoption of new technologies in recent years. There are several types of bridge inspections, each designed to address specific concerns. Here’s an overview: While visual inspections are the most common, other advanced techniques help uncover hidden issues: Each technique has its advantages, and choosing the right one depends on the type of bridge and the specific concerns being addressed. Bridge inspections are not without their difficulties. Some of the main challenges include: To overcome these challenges, many organizations are turning to drone technology, which can access hard-to-reach areas safely and efficiently. Every country has its own set of regulations governing bridge inspections. These rules typically outline: In the U.S., the Federal Highway Administration (FHA) sets national standards through the National Bridge Inspection Standards (NBIS). For example: States may also add additional requirements, such as expanding the scope of bridges to inspect or increasing the frequency of checks. During an inspection, an inspector looks for signs of deterioration, such as cracks, rust, or movement in the structure. They also check bearings, supports, and electrical systems, which are often overlooked but crucial for long-term safety. Electrical infrastructure, including wiring and utility connections, must be examined carefully. Any outdated or damaged wiring could pose a risk to both the bridge and the people who use it. Bridge inspectors usually need formal certification to conduct inspections legally. In the U.S., the FHA oversees training programs that meet the National Bridge Inspection Standards (NBIS). Proper certification ensures that inspectors are trained to recognize and report potential hazards accurately. This is essential for maintaining public trust and compliance with legal requirements. Most countries define bridge inspection procedures through specific standards. In the U.S., the Federal Highway Administration outlines detailed criteria for how inspections should be conducted, covering everything from maintenance policies to guidance for different inspection types.
We have different Silicone Fluid, silicone oil for different industries.
dimethyl silicone oil: lubrication, shakeproof, electric insulating oil, defoamer,mould release, cosmetics.rubber and plastic, heat-conducting medium etc.
vinyl silicone oil: silicone rubber compound
hydroxy silicone oil: aids for silicone rubber, waterproof,softner and antiadhesive agent for fabric,paper and leather
amino silicone oil: fabric(terylene/polyester)softer treatment, Fabric; textile, Cosmetics, improve hair combed ,Slippery and shining .
phenyl silicone oil: Insulation, lubrication, damping, quakeproof, moistureproof, dustproof, high temperature hydraulic fluid, High temperature heat carrier, filling oil for Transformer and pressure signals transferring medium for various pressure transmitter.
hydrogen silicone oil: aids for silicone rubber, waterproof,softner and antiadhesive agent for fabric,paper and leather.
Polyether Silicone Oil: silicone surfactant, textile adjuvant,etc
The role of silicone in rubber, plastic and metal demoulding Silicon Fluid, silicon oil, dimethyl silicone oil, vinyl silicone oil, hydroxy silicone oil, amino silicone oil, phenyl silicone oil, hydrogen silicone oil, Polyether Silicone Oil Changzhou Dahua-Luckypower , https://www.czluckypowertech.comBridge Inspections — Everything You Need to Know
BRIDGE INSPECTIONS ARE A CRUCIAL PART OF MAINTAINING KEY INFRASTRUCTURE AND ENSURING SAFETY—LEARN MORE ABOUT THEM IN THIS GUIDE.

What is a Bridge Inspection?
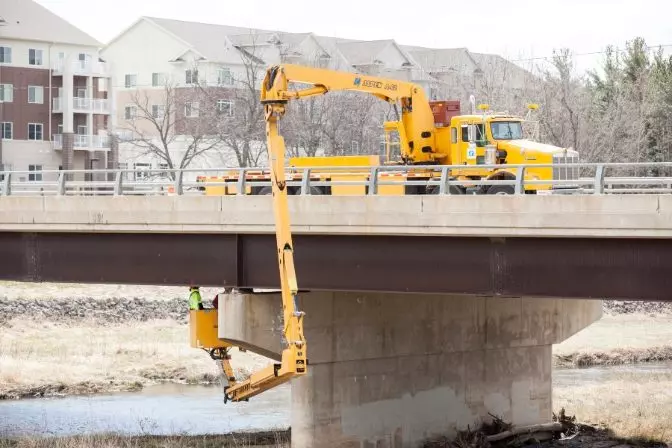

Bridge Inspection Types, Techniques, and Challenges
BRIDGE INSPECTION TECHNIQUES
UNIQUE CHALLENGES FOR BRIDGE INSPECTIONS
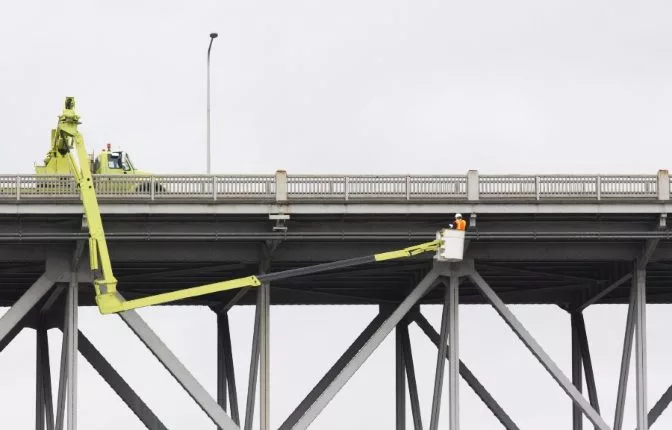

Regulatory Considerations for Bridge Inspections
What Does a Bridge Inspector Do?
BRIDGE INSPECTION CERTIFICATION
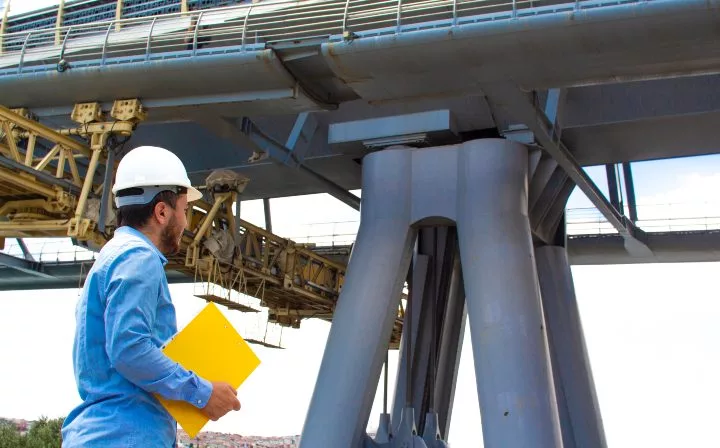

BRIDGE INSPECTION STANDARDS
Because of the non-stick property of dimethyl silicone oil and rubber, plastic, metal, etc., it can be used for the demoulding of polyurethane microporous elastomer molded products, but also can be used for the demoulding of peeling polyurethane molded products, rubber products, ABS molded products, etc. The main advantages of the release agent are small release force, no pollution, convenient transportation, and make the surface of the product clean, smooth, clear texture. With the rapid development of polyurethane industry, silicone oil release agent market is expanding.